Case Study: 10x Organic Traffic Growth for B2B SaaS

The SEO landscape is changing. A few years ago, the formula was simple. Structure your site properly and deliver compelling content, and traffic will follow.
After an onslaught of updates, Google has changed this formula. Keyword density, alt-tags, and even site structure have taken a back seat to CTR (click through rate), time on page, and user engagement. Structure has become far less important than user interaction. Every update for the past year has oriented ranking favorability to (E‑E‑A‑T) expertise, experience, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness.
Gemini summaries, Chat GPT, and other LLMs have also created massive upheaval in how users interact with search.
Companies that have relied on casting a wide net by creating helpful, listicle type articles to appeal to a massive audience are being eviscerated by more specific content and AI summaries. Take a look at Hubspot over the past 5 years:
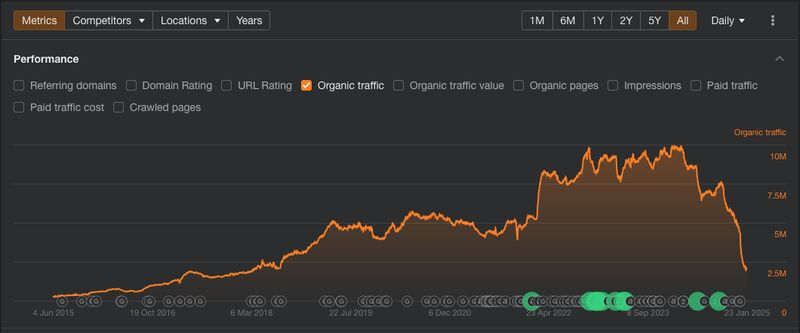
These summaries have created an environment where impressions are cheap but clicks are rare. SEO is no longer the formulaic practice of keyword research, backlink farming, and technical content optimization. It has morphed into a much more experimental process that requires a creative approach.
It is time to create a new playbook for SEO. One that implements optimization for LLM's without cannibalizing results in traditional search.
Creating a New Approach for B2B SaaS SEO
Last year, I began work optimizing a site for a mid-sized SaaS company. While they had a great market offering, their website traffic was peaking at around 200 users a month. The users they were receiving seemed confused and were not converting.
I was brought on for 2-4 hours a week to...
- rank for high-value, non-branded terms
- increase organic traffic to 1,000 relevant users a month
- improve site health and backlink profile
- improve UX metrics such as time on page and engagement
- implement SEO analytics
- assist in building a content engine that delivers relevant, high ranking content
After one year, the internally team and I had increased organic traffic to ~2,600 monthly users. We greatly improved site health, site speed, and backlink profile health. We piloted new content campaigns, and increased all relative metrics regarding user engagement. We built a backlink engine to capture high quality links from relevant, authoritative sources.
After 8 months, we had built a solid foundation of traffic coming from relevant searches and referral sources.
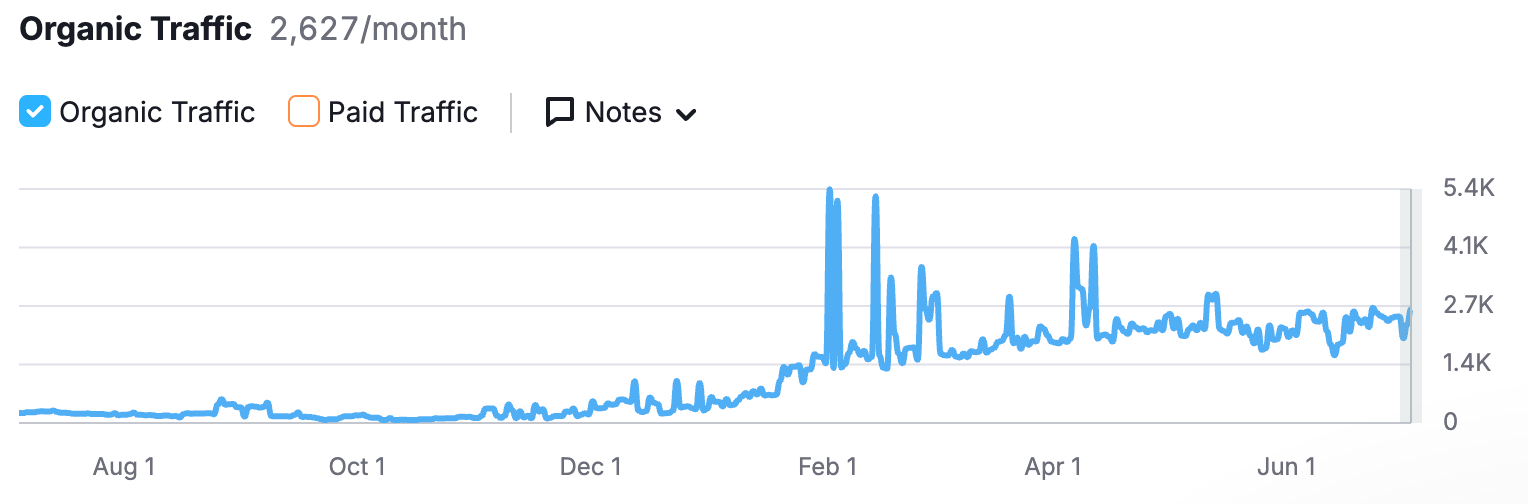
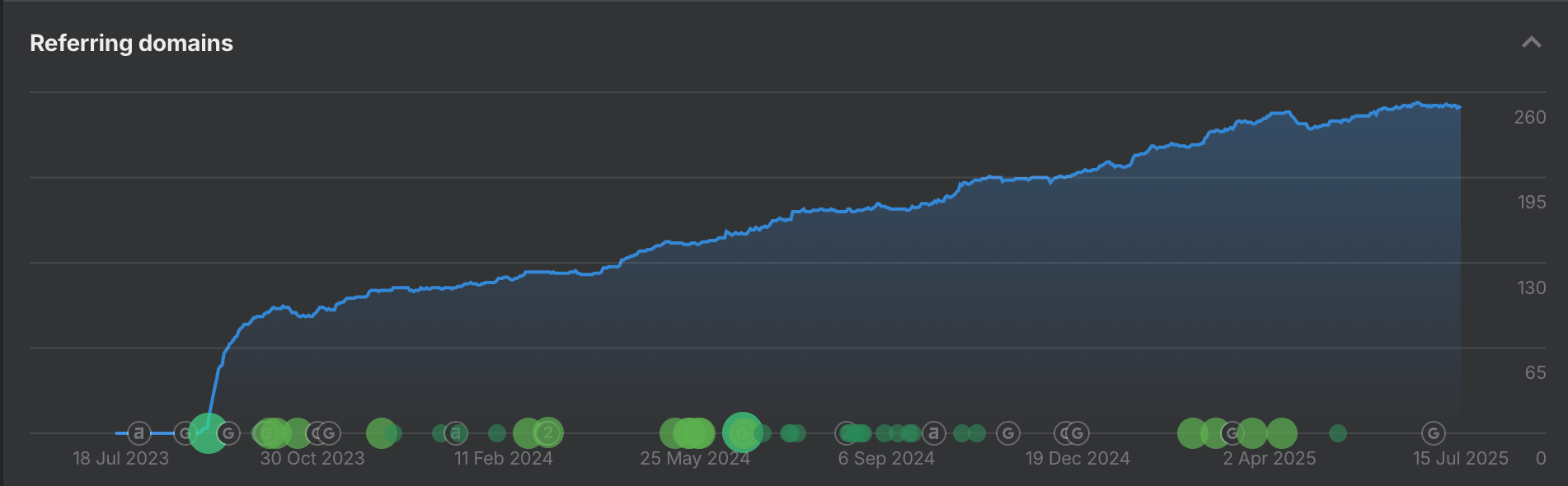
Most importantly, we tried (and often failed) at developing new methods of driving traffic to a highly specialized, industry specific SaaS product. This ongoing process of trial and error carried the project to success, and I believe will continue to show outsized ROI for the sites SEO prowess into the future.
Phase One: Analytics and Low Hanging Fruit
Full-Spectrum Analytics Setup and Audit
This project started with creating clear objectives and building data dashboards. We integrated Google Analytics, Search Console, SEMrush and Ahrefs (later Clearscope and Fullstory). These data streams began to tell us a story of how customers were currently finding and interacting with the website.
An onsite (Webflow) audit was conducted to identify low hanging fruit opportunities. This revealed a need for some minor structure changes and an overhaul to alt-tags. We updated headers and URL structure to be more inline with a long term strategy of ranking for relevant keywords.
The team and I also made site wide changes...
- Fixing backlink health
- Updating internal linking practices
- To high value keyword density
- Eliminating 404 error fixes
- Eliminating orphan pages
- Updating Bad redirects
We saw an immediate 40% increase in organic traffic after implementing these updates, and quickly took the #1 spot for our primary non-branded keyword target. This phase patched up the more urgent issues and created a platform to launch into more ambitious territory.
Site health is an easy metric to neglect. It is boring to update and can sometimes have very little immediate effect on traffic. However when it is neglected, it becomes impossible to scale. Bad-redirects, toxic backlinks, orphan pages, and 404 errors, all signal to Google that a site is not worth ranking.
Google (and LLM's) are constantly trying to avoid user frustration. They will hesitate to send anyone to a site that is not fast and well structured. By making these changes we improved UX while signaling to Google that this site was useful and easy to use for users looking for industry specific answers.
This change boosted site health (an Ahrefs proprietary metric) from the low 70s to a 95).
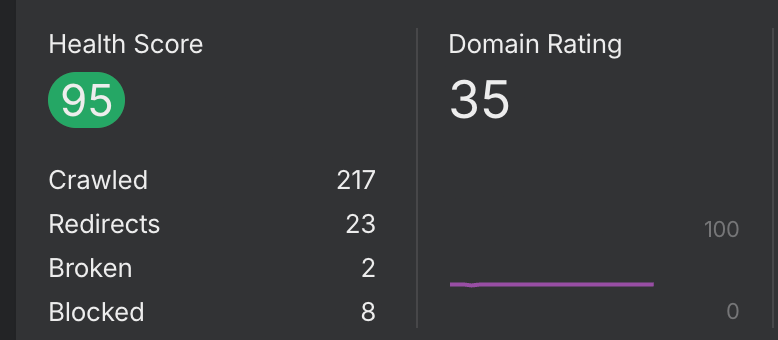
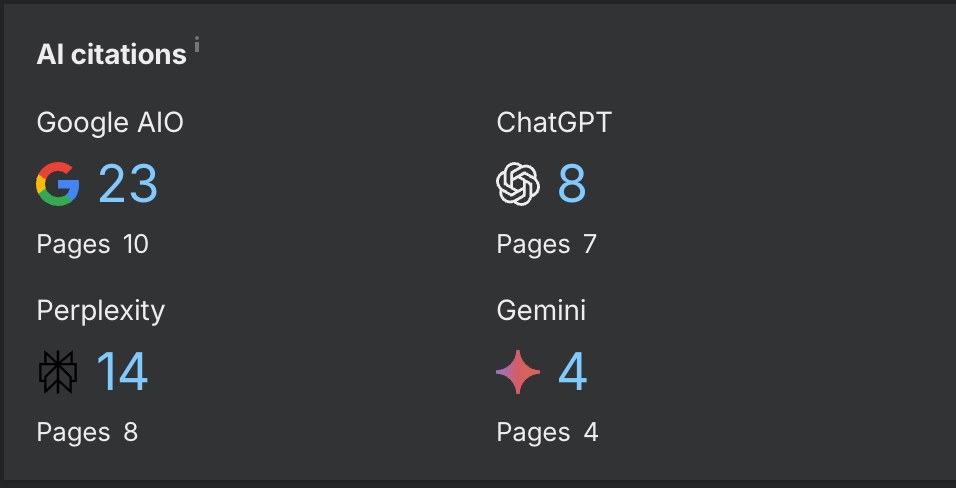
Updating the structure also made the site content friendlier to AI models. Ideal site schema for LLM optimization is still a bit of a black box, but through trial and error we have begun to pull back the curtain. Although this was originally unintentional, it helped later develop a process for optimizing content for AI citation. This project now benefits from a number of AI citations that drive organic traffic to the site.
In fact, LLM's are now our 3rd most popular referral source for new users (behind Google and Bing).
Phase 2: Creating and Implementing a New Approach to Content
New Kinds of Content
The organization's current approach to content was not delivering the desired results. Much of the offering was based on company news, partnerships, and case studies for clients. This was valuable content for creating legitimacy, but was not raking well in search.
We found a formula for content that filled these gaps. By focusing on viral topics in context of our SaaS product, we drove relevant traffic to helpful and engaging articles.
Google loves to recommend websites that provide readers real value. When building a content strategy for SEO, companies need to find the intersection between what people want to read, and the unique perspective they are able to offer.
These articles positioned the company as an industry thought leader and provided actual value. Traffic skyrocketed as a result. These 'viral topic' articles soon became our highest performers with hundreds of thousands of impressions, and thousands of clicks. We were able to identify many of the users as high priority leads from companies that could directly benefit from the product on offer.
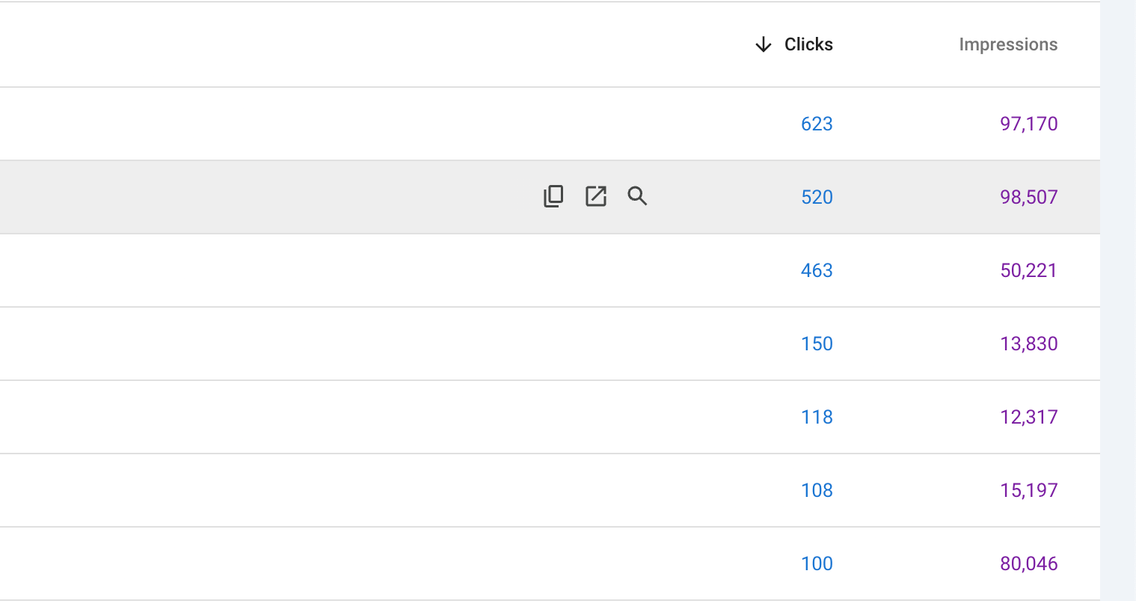
We also created highly specific 'how-to' articles to help solve problems related to our industry. These drove whole categories of keywords that we were otherwise unable to rank for. By addressing specific, highly frustrating problems directly, we captured users in the problem solving phase. Capturing leads in this stage increases time-on-page, and signals to Google that the article solved a real problem.
The success we found formed into somewhat of a content hypothesis for the age of AI.
Content must either be...
- Hyper-clear and helpful to someone experiencing a problem they need solved now. (Like a how-to, or a definition to an industry specific word)
- Genuinely enjoyable to read
AI is really good at solving specific problems in context, but it needs to get it's information from somewhere. By going niche and writing with clarity, we were able to be that source for a number of topics.
AI is really bad at showing people things they did not specifically ask for. Users do not use AI to 'stumble upon' new content or ideas. Even in todays over saturated content market, we were able to break through by delivering content that sparked genuine curiosity.
Creating a Glossary
Using this momentum, we also created a glossary section for more robust internal linking and to create traffic from users researching industry specific terms:
This glossary is still in development as is increasing impressions and clicks week over week. As we continue to add words, we expect the growth to continue and the glossary section to add a steady, evergreen drip to relevant web traffic.
The glossary section has also proven to be a huge asset in ranking in LLM citation. AI models prioritize shorter, hyper-clear content and a glossary section fits this criteria perfectly. After experimenting with structure we found that this structure performed well in LLM's without sacrificing traditional search performance:
Term Title: (What is 'Your Term')
Synonyms: (place terms here)
High level summery: Two or three sentences that define your term in the clearest way imaginable. No branded words, links, or anything else to muddy the waters. Just the most accessible and industry specific definition you can develop.
Full Definition: The in depth version of what you just gave.
Challenges: The common challenges associated with your term. This section is designed to help associate your link with people who are looking for solutions to their specific problem. Many use LLM's to solve in context problems. This will help you be the link that is used when people are searching for a solution via generative AI.
Your Role: The branded part. This is where you talk about how the term relates to your brand specifically.
Related terms: Allows the user to click through to other related terms. Increases CTR and engagement.
Related Content: More opportunity to CTR and engagement with your other content that mentions this term or similar terms.
Using this structure we are continually testing what terms preform the best to inform future decision making on which terms to implement. Early signs point to technical terms referencing specific components or systems working the best.
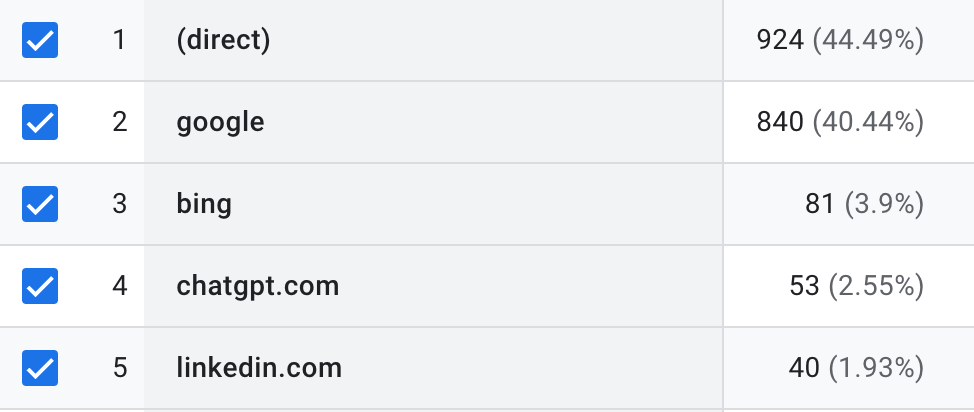
After implementing the glossary we have seen a climb in traffic coming from ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, and DeepSeek. I am not sure that this correlation is a causation, but will continue to monitor.
ChatGPT is now one of our highest referral sources for traffic:
Creating more interactivity
Getting a higher on site CTR (Click Through Rate) became a priority when Google pushed a major update to search emphasizing CTR, and time-on-page over other previously important metrics. To create a higher level of user engagement we are testing creating interactive tools to be embedded inline in content. These tools are custom developed to make articles more interactive, engaging, and helpful.
A few years ago, developing interactive tools just to make content more helpful was not a viable content strategy. Due to AI, development time has been massively compressed and the creation of these tools is feasible and simple to implement.
Development and testing of best practices for these tools is ongoing. Google loves good user engagement and we believe these will be a huge advantage in achieving that.
Results (ongoing)
Traffic:
- 13x organic traffic growth year-over-year
- Stabilized around 2,600+ monthly sessions, with significantly higher qualified intent
- Increased content performance for long-tail and mid-funnel queries
Referring Domain Growth:
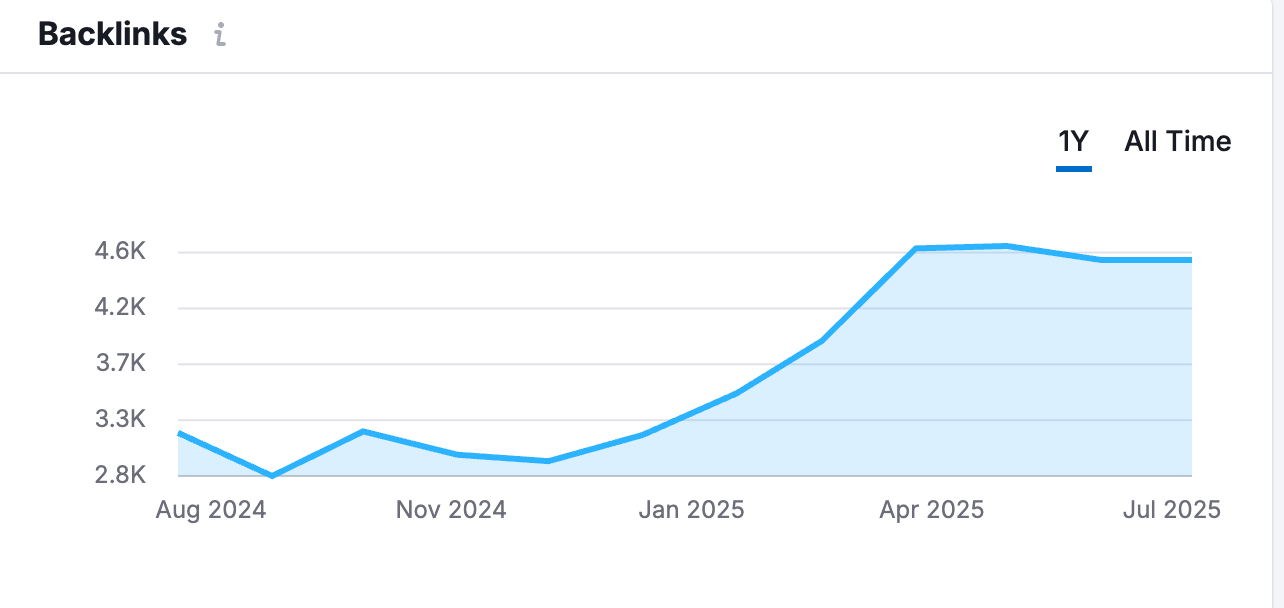
- Organically doubled backlinks
- Strategic glossary content earned backlinks and LLM citations from knowledge aggregators
- Referring domain average domain authority has increased by 7+ points
Final Takeaways
This project proves that technical SEO and content strategy, when aligned with modern AI search behavior, can produce outsized results in highly competitive SaaS markets. This success came from executing a layered, data-backed strategy built to evolve with how users search today.
The most important asset to this project was an attitude of experimentation. The SEO world is currently the wild west. Testing new methods often failed, but when we found what worked, we doubled down to great effect.
During this process, I found that many of the available tools for analyzing keywords and content for AI optimization and snippets, were insufficient. To close this gap, I developed and launched my own suite of tools that I am making available to all my clients. It is still in beta, and can be tested here:
If interested in pursuing an engagement, please contact me here:

